- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 11 DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
EXKIVITY is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion mutations, as detected by an FDA-approved test [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)], whose disease has progressed on or after platinum-based chemotherapy.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate and duration of response [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trial(s).
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Evaluation and Testing Before Initiating EXKIVITY
Before initiating EXKIVITY, evaluate QTc and electrolytes and correct abnormalities in sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.2 Patient Selection
Select patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC for treatment with EXKIVITY based on the presence of EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Information on FDAapproved tests is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
2.3 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of EXKIVITY is 160 mg orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Take EXKIVITY with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology 12.3], at the same time each day. Swallow EXKIVITY capsules whole. Do not open, chew or dissolve the contents of the capsules.
If a dose is missed by more than 6 hours, skip the dose and take the next dose the following day at its regularly scheduled time.
If a dose is vomited, do not take an additional dose. Take the next dose as prescribed the following day.
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
EXKIVITY dose reduction levels for adverse reactions are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1: Recommended EXKIVITY Dose Reductions
| Dose Reductions | Dose Level |
|---|---|
| First dose reduction | 120 mg once daily |
| Second dose reduction | 80 mg once daily |
Recommended dosage modifications of EXKIVITY for adverse reactions are provided in Table 2.
Table 2: Recommended Dosage Modifications for EXKIVITY Adverse Reactions
| Adverse Reaction | Severity* | EXKIVITY Dosage Modification |
| QTc Interval Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] |
Grade 2 (QTc interval 481-500 msec) |
First Occurrence
|
|
Grade 3 (QTc interval ≥501 msec or QTc interval increase of >60 msec from baseline) |
First Occurrence
|
|
|
Grade 4 (Torsades de Pointes; polymorphic ventricular tachycardia; signs/symptoms of serious arrhythmia) |
|
|
| Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | Any grade |
|
| Decreased Ejection Fraction or Heart Failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] |
Grade 2 decreased ejection fraction |
|
| ≥ Grade 2 heart failure or Grade 3 or 4 decreased ejection fraction |
|
|
| Diarrhea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] | Intolerable or recurrent Grade 2 or Grade 3 |
|
| Grade 4 |
First Occurrence
|
|
| Increased Amylase or Lipase [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] | Grade 3 without signs or symptoms |
|
| Grade 3 with signs or symptoms |
|
|
| Grade 4 |
First Occurrence
|
|
| Other AdverseReactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] | Intolerable or recurrent Grade 2 or Grade 3 |
|
|
Grade 4 |
First Occurrence
|
ULN = upper limit of normal
* Graded per Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events Version 5.0
2.5 Dosage Modifications for Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors
Avoid concomitant use of moderate CYP3A inhibitors with EXKIVITY. If concomitant use of a moderate CYP3A inhibitor cannot be avoided, reduce the EXKIVITY dose by approximately 50% (i.e., from 160 to 80 mg, 120 to 40 mg, or 80 to 40 mg) and monitor the QTc interval more frequently. After the moderate CYP3A inhibitor has been discontinued for 3 to 5 elimination half-lives, resume EXKIVITY at the dose taken prior to initiating the moderate CYP3A inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
2.6 Dosage Modifications for Patients with Severe Renal Impairment
Reduce the EXKIVITY dose by approximately 50% (i.e., from 160 to 80 mg, 120 to 40 mg, or 80 to 40 mg) and monitor the QTc interval more frequently for patients with severe renal impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules: 40 mg, white, size 2, imprinted with “MB788” on the cap and “40mg” on the body in black ink.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 QTc Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes
EXKIVITY can cause life-threatening heart rate-corrected QT (QTc) prolongation, including Torsades de Pointes, which can be fatal. In the 250 patient subset of the pooled EXKIVITY safety population who had scheduled and unscheduled electrocardiograms (ECGs) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)], 1.2% of patients had a QTc interval >500 msec and 11% of patients had a change-from-baseline QTc interval >60 msec. Grade 4 Torsades de Pointes occurred in 1 patient (0.4%). Clinical trials of EXKIVITY did not enroll patients with baseline QTc greater than 470 msec.
Assess QTc and electrolytes at baseline and correct abnormalities in sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium prior to initiating EXKIVITY. Monitor QTc and electrolytes periodically during treatment. Increase monitoring frequency in patients with risk factors for QTc prolongation, such as patients with congenital long QT syndrome, heart disease, severe renal impairment, or electrolyte abnormalities. Avoid use of concomitant drugs which are known to prolong the QTc interval. Avoid concomitant use of strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors with EXKIVITY [see Drug Interactions (7.1)], which may further prolong the QTc [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue EXKIVITY based on the severity of the QTc prolongation [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.2 Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis
EXKIVITY can cause ILD/pneumonitis, which can be fatal. In the pooled EXKIVITY safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], ILD/pneumonitis occurred in 4.3% of patients including 0.8% Grade 3 events and 1.2% fatal events.
Monitor patients for new or worsening pulmonary symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis. Immediately withhold EXKIVITY in patients with suspected ILD/pneumonitis and permanently discontinue EXKIVITY if ILD/pneumonitis is confirmed [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.3 Cardiac Toxicity
EXKIVITY can cause cardiac toxicity (including decreased ejection fraction, cardiomyopathy, and congestive heart failure) resulting in heart failure which can be fatal. In the pooled EXKIVITY safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], heart failure occurred in 2.7% of patients including 1.2% Grade 3 reactions, 0.4% Grade 4 reactions, and one (0.4%) fatal case of heart failure.
EXKIVITY can cause QTc prolongation resulting in Torsades de Pointes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Atrial fibrillation (1.6%), ventricular tachycardia (0.4%), first degree atrioventricular block (0.4%), second degree atrioventricular block (0.4%), left bundle branch block (0.4%), supraventricular extrasystoles (0.4%) and ventricular extrasystoles (0.4%) also occurred in patients receiving EXKIVITY.
Monitor cardiac function, including assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction at baseline and during treatment. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue EXKIVITY based on the severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.4 Diarrhea
EXKIVITY can cause diarrhea, which can be severe. In the pooled EXKIVITY safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], diarrhea occurred in 93% of patients, including 20% Grade 3 and 0.4% Grade 4. The median time to first onset of diarrhea was 5 days but diarrhea has occurred within 24 hours after administration of EXKIVITY. In the 48% of patients whose diarrhea resolved, the median time to resolution was 3 days. Diarrhea may lead to dehydration or electrolyte imbalance, with or without renal impairment. Treat diarrhea promptly.
Advise patients to start an antidiarrheal agent (e.g., loperamide) at first sign of diarrhea or increased bowel movement frequency and to increase fluid and electrolyte intake.
Monitor electrolytes and withhold, reduce the dose or permanently discontinue EXKIVITY based on the severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.5 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, EXKIVITY can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Oral administration of mobocertinib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis resulted in embryolethality at maternal exposures approximately 1.7 times the human exposure based on area under the curve (AUC) at the 160 mg once daily clinical dose.
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective non-hormonal contraception during treatment with EXKIVITY [see Drug Interactions (7.2)] and for 1 month after the last dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with EXKIVITY and for 1 week after the last dose of EXKIVITY [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:- QTc Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Cardiac Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Diarrhea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The pooled safety population described in WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflects exposure to EXKIVITY as a single agent at a dose of 160 mg orally once daily in 256 patients, including 114 patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation-positive locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC from Study AP32788-15-101, and patients with other solid tumors. Forty-eight percent (48%) were exposed for 6 months or longer and 12% were exposed for greater than one year. The most common (>20%) adverse reactions were diarrhea, rash, nausea, stomatitis, vomiting, decreased appetite, paronychia, fatigue, dry skin, and musculoskeletal pain. The most common (≥2%) Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities were decreased lymphocytes, increased amylase, increased lipase, decreased potassium, decreased hemoglobin, increased creatinine, and decreased magnesium
EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutation-Positive Locally Advanced or Metastatic NSCLC Previously Treated with Platinum-Based Chemotherapy
The safety of EXKIVITY was evaluated in a subset of patients in Study AP32788-15-101 with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation-positive locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who received prior platinum-based chemotherapy [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Patients with a history of interstitial lung disease, drug-related pneumonitis, radiation pneumonitis that required steroid treatment; significant, uncontrolled, active cardiovascular disease; or prolonged QTc interval were excluded from enrollment in this trial. A total of 114 patients received EXKIVITY 160 mg once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity; 60% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 14% were exposed for greater than 1 year.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 46% of patients who received EXKIVITY. Serious adverse reactions in ≥2% of patients included diarrhea, dyspnea, vomiting, pyrexia, acute kidney injury, nausea, pleural effusion, and cardiac failure. Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1.8% of patients who received EXKIVITY, including cardiac failure (0.9%), and pneumonitis (0.9%).
Permanent discontinuation occurred in 17% of patients who received EXKIVITY. Adverse reactions requiring permanent discontinuation of EXKIVITY in at least ≥2% of patients were diarrhea and nausea.
Dosage interruptions of EXKIVITY due to an adverse reaction occurred in 51% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in >5% of patients included diarrhea, nausea and vomiting.
Dose reductions of EXKIVITY due to an adverse reaction occurred in 25% of patients. The adverse reaction requiring dose reduction in >5% of patients was diarrhea.
Table 3 summarizes the adverse reactions in Study AP32788-15-101.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions (≥10%) in Patients with EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutation-Positive NSCLC Whose Disease Has Progressed on or after Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Study AP32788-15-101
| Adverse Reaction | EXKIVITY (N = 114) | |
| All Grades* (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
| Diarrhea | 92 | 22 |
| Stomatitisa | 46 | 4.4** |
| Vomiting | 40 | 2.6** |
| Decreased appetite | 39 | 0.9** |
| Nausea | 37 | 4.4** |
| Decreased weight | 21 | 0 |
| Abdominal painb | 18 | 1.8** |
| Gastroesophageal reflux disease | 15 | 0 |
| Dyspepsia | 11 | 0 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||
| Rashc | 78 | 1.8** |
| Paronychiad | 39 | 0.9** |
| Dry skin | 32 | 0 |
| Pruritus | 24 | 0.9** |
| Alopecia | 19 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||
| Musculoskeletal paine | 34 | 2.6** |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||
| Fatiguef | 29 | 3.5** |
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders | ||
| Coughg | 24 | 0 |
| Upper respiratory tract infectionh | 16 | 0 |
| Dyspneai | 15 | 4.4 |
| Rhinorrhea | 13 | 0 |
| Eye Disorders | ||
| Ocular Toxicityj | 11 | 0 |
| Cardiac Disorders | ||
| QTc interval prolongationk | 10 | 3.5 |
| Hypertensionl | 10 | 4.4** |
| Nervous System Disorders | ||
| Headache | 10 | 0 |
* Graded according to National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE 5)
** Events of Grade 3 only (no Grade 4 occurred)
a Stomatitis includes angular cheilitis, aphthous ulcer, cheilitis, mouth ulceration, mucosal inflammation, odynophagia,
and stomatitis.
b Abdominal pain includes abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal tenderness, and
gastrointestinal pain.
c
Rash includes acne, dermatitis, dermatitis acneiform, rash, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, rash papular, rash
pruritic, rash pustular, and urticaria.
d Paronychia includes nail bed tenderness, nail disorder, nail infection, onycholysis, and paronychia.
e Musculoskeletal pain includes arthralgia, back pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal discomfort,
musculoskeletal pain, myalgia, neck pain, non-cardiac chest pain, pain in extremity, and spinal pain.
f
Fatigue includes asthenia, and fatigue.
g Cough includes cough, productive cough, and upper-airway cough syndrome.
h Upper respiratory tract infection includes nasopharyngitis, pharyngitis, respiratory tract infection, rhinitis, sinusitis, and
upper respiratory tract infection.
i
Dyspnea includes dyspnea, and dyspnea exertional.
j
Ocular toxicity includes dry eye, eye pruritus, abnormal sensation in eye, eye discharge, blepharitis, trichiasis,
conjunctival hemorrhage, vitreous floaters, blurred vision and corneal edema.
k
QTc interval prolongation includes electrocardiogram QT prolonged, and ventricular arrhythmia.
l Hypertension includes blood pressure increased, and hypertension.
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in <10% of patients receiving EXKIVITY included edema (9%), acute kidney injury (8%), peripheral neuropathy (7%), palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (4.4%), pneumonitis (2.6%) and cardiac failure (2.6%).
Table 4 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in Study AP32788-15-101.
Table 4: Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥20%) Worsening from Baseline in Patients with EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutation-Positive NSCLC Whose Disease Has Progressed on or after Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Study AP32788-15-101
| Laboratory Abnormality |
EXKIVITY** (N = 114) |
|
| All Grades* (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | |
| Hematology | ||
| Decreased red blood cells | 59 | 3.5 |
| Decreased lymphocytes | 52 | 15 |
| Decreased platelets | 26 | 0.9 |
| Decreased leukocytes | 25 | 0 |
| Chemistry | ||
| Increased creatinine | 52 | 2.7 |
| Increased amylase | 40 | 13 |
| Increased lipase | 35 | 10 |
| Decreased potassium | 29 | 5 |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 25 | 1.8 |
| Decreased albumin | 23 | 1.8 |
| Decreased magnesium | 23 | 2.7 |
| Increased alanine aminotransferase | 22 | 2.7 |
| Increased aspartate aminotransferase | 21 | 1.8 |
| Decreased sodium | 20 | 0.9 |
* Grades per NCI CTCAE v5.0
** The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 93 to 113 based on the number of patients with a
baseline and at least one post-treatment value. The laboratory abnormalities are values that reflect
worsening from baseline.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on EXKIVITY
| Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors | |
| Clinical Impact |
|
|
Prevention or Management |
|
| Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inducers | |
| Clinical Impact |
|
| Prevention or Management |
|
7.2 Effect of EXKIVITY on Other Drugs
| CYP3A Substrates | |
| Clinical Impact |
|
| Prevention or Management |
|
7.3 Drugs that Prolong the QTc Interval
| Drugs that Prolong the QTc Interval | |
| Clinical Impac |
|
| Prevention or Management |
|
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology
(12.1)], EXKIVITY can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no
available data on EXKIVITY use in pregnant women. Oral administration of mobocertinib to pregnant
rats during the period of organogenesis resulted in embryolethality (embryo-fetal death) and maternal
toxicity at plasma exposures approximately 1.7 times the human exposure based on AUC at the
160 mg once daily clinical dose (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study, once daily oral administration of mobocertinib to pregnant rats
during the period of organogenesis resulted in maternal toxicity (reduced body weight gain and food
consumption) at 10 mg/kg (approximately 1.7 times the human exposure based on AUC at the
160 mg once daily clinical dose). Adverse effects on embryo-fetal development at this dose level included embryolethality due to post-implantation loss (embryo-fetal death) and effects on fetal
growth (decreased fetal weights). There was no clear evidence of fetal malformations at the high
dose level (10 mg/kg).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of mobocertinib or its metabolites in human milk or their effects on
the breastfed child or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in
breastfed children, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with EXKIVITY and for 1 week
after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
EXKIVITY can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating EXKIVITY.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective non-hormonal contraception during treatment with EXKIVITY and for 1 month after the last dose. EXKIVITY may render hormonal contraceptives ineffective [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Males
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during
treatment with EXKIVITY and for 1 week after the last dose.
Infertility
Based on animal studies, EXKIVITY may impair fertility in males and females of reproductive potential
[see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of EXKIVITY in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 114 patients [see Clinical Studies (14)] who received EXKIVITY in clinical studies, 37% were 65 years and over, and 7% were 75 years and over. No overall difference in effectiveness was observed between patients aged 65 and older and younger patients. Exploratory analysis suggests a higher incidence of Grade 3 and 4 adverse reactions (69% vs 47%) and serious adverse reactions (64% vs 35%) in patients 65 years and older as compared to those younger than 65 years.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Mobocertinib plasma concentrations are higher in patients with severe renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of adverse reactions. Reduce the recommended dosage of EXKIVITY for patients with severe renal impairment (estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 by Modification of Diet in Renal Disease [MDRD] equation) [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. No dosage adjustment of EXKIVITY is recommended for patients with mild-to-moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30 to 89 mL/min/1.73 m2 by MDRD equation).8.7Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment of EXKIVITY is recommended for patients with mild (total bilirubin ≤ upper limit of normal [ULN] and aspartate aminotransferase [AST] > ULN or total bilirubin >1 to 1.5 times ULN and any AST)-to-severe (total bilirubin >3 times ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].11 DESCRIPTION
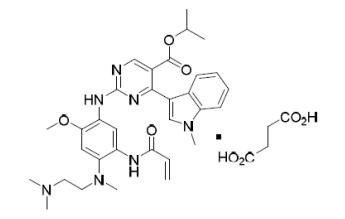
Mobocertinib is a kinase inhibitor. The chemical name for mobocertinib succinate is propan-2-yl 2-[5- (acryloylamino)-4-{[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl](methyl)amino}-2-methoxyanilino]-4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3- yl)pyrimidine-5-carboxylate succinate. The molecular formula is C32H39N7O4 + C4H6O4 (succinate salt) which corresponds to a molecular weight of 703.8 g/mol. Mobocertinib has no chiral centers. The chemical structure of mobocertinib succinate is shown below:
Mobocertinib succinate has a solubility of 152 mg/mL in pH 1.0 and >17.6 mg/mL in pH 6.8 solutions at 37°C.
EXKIVITY capsule for oral administration contains 40 mg mobocertinib equivalent to 48.06 mg mobocertinib succinate, with no inactive ingredients. The capsule shells contain gelatin and titanium dioxide. The printing ink contains shellac, dehydrated alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, strong ammonia solution, black iron oxide, potassium hydroxide, and purified water.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Mobocertinib is a kinase inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) that irreversibly binds to and inhibits EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations at lower concentrations than wild type (WT) EGFR. Two pharmacologically-active metabolites (AP32960 and AP32914) with similar inhibitory profiles to mobocertinib have been identified in the plasma after oral administration of mobocertinib. In vitro, mobocertinib also inhibited the activity of other EGFR family members (HER2 and HER4) and one additional kinase (BLK) at clinically relevant concentrations (IC50 values <2 nM).
In cultured cell models, mobocertinib inhibited the proliferation of cells driven by different EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation variants at 1.5- to 10-fold lower concentrations than WT-EGFR signaling inhibition.
In animal tumor implantation models, mobocertinib exhibited anti-tumor activity against xenografts with the EGFR exon 20 insertions NPH or ASV.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Mobocertinib exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamic response are unknown.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The largest mean increase in QTc was 23.0 msec (UCI: 25.5 msec) following administration of
EXKIVITY 160 mg once daily. The increase in QTc interval was concentration-dependent.
The largest mean increase in the PR interval was 12.4 msec (UCI: 15.0 msec). PR interval prolongation >220 msec occurred in 5% of patients taking EXKIVITY 160 mg once daily.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
After single- and multiple-dose administration, combined molar Cmax and AUC0-24h of mobocertinib and its active metabolites, AP32960 and AP32914, was dose-proportional over the dose range of 5 to 180 mg once daily (0.03 to 1.1 times the approved recommended dosage). No clinically meaningful accumulation was observed after administration of EXKIVITY 160 mg once daily based on the AUC ratio of mobocertinib.
Absorption
The median (min, max) time to peak concentration (Tmax) of mobocertinib is 4 hours (1, 8 hours). The
mean (%CV) absolute bioavailability is 37% (50%).
Effect of Food
No clinically meaningful differences in the combined molar AUC and Cmax of mobocertinib, AP32960,
and AP32914 were observed following administration of a high-fat meal (approximately 900 to
1000 calories, with 150 calories from protein, 250 calories from carbohydrate and 500 to 600 calories
from fat) or a low fat-meal (approximately 336 calories, with 37 calories from protein, 253 calories
from carbohydrate, and 46 calories from fat) compared to administration after an overnight fast.
Distribution
Mobocertinib was bound to human plasma proteins in a concentration independent manner in vitro from 0.5 to 5.0 μM. The mean (standard deviation) bound fraction was 99.3% (0.11%) for mobocertinib, 99.5% (0.16%) for AP32960 and 98.6% (0.36%) for AP32914 in vitro.
The blood-to-plasma ratio was 0.76 for mobocertinib, 1.2 for AP32960 and 0.71 for AP32914.
The mean (%CV) apparent volume of distribution (Vss/F) of mobocertinib was 3,509 L (38%) at steady-state.
Elimination
The mean (%CV) plasma elimination half-life of mobocertinib was 18 hours (21%) at steady-state.
The mean apparent oral clearance (CL/F) (%CV) of mobocertinib was 138 L/hr (47%) at steady-state.
The mean (%CV) plasma elimination half-life of AP32960 was 24 hours (20%) at steady-state.
The
mean apparent oral clearance (CL/F) (%CV) of AP32960 was 149 L/hr (36%) at steady-state.
The mean (%CV) plasma elimination half-life of AP32914 was 18 hours (21%) at steady-state.
The
mean apparent oral clearance (CL/F) (%CV) of AP32914 was 159 L/hr (52%) at steady-state.
Metabolism
Mobocertinib is primarily metabolized by CYP3A. The two active metabolites, AP32960 and
AP32914, are equipotent to mobocertinib and account for 36% and 4% of the combined molar AUC,
respectively.
Excretion
Following administration of a single 160 mg oral dose of radiolabeled mobocertinib, approximately
76% of the dose was recovered in feces (approximately 6% as unchanged mobocertinib) and
approximately 4% was recovered in urine (approximately 1% as unchanged mobocertinib). The percentage of the administered dose recovered in feces and urine for AP32960 was approximately
12% and 1%, respectively. The metabolite AP32914 was below the detection limit in urine and feces.
Specific Populations
No clinically meaningful differences in the pharmacokinetics of mobocertinib were observed based on
age (18 to 86 years), race (White, Black, Asian), sex, body weight (37.3 to 132 kg), mild-to-moderate
renal impairment (eGFR 30 to 89 mL/min/1.73 m2 by MDRD equation), or mild (total bilirubin ≤ ULN
and AST > ULN or total bilirubin >1 to 1.5 times ULN and any AST)-to-severe (total bilirubin >3 times
ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment.
Patients with Renal Impairment
Following administration of a single 80 mg oral dose of EXKIVITY, the unbound combined molar AUC
of mobocertinib and its active metabolites was increased by 112% in subjects with severe renal
impairment (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 by MDRD equation) as compared to subjects with normal
renal function (eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73 m2 by MDRD equation).
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model-Informed Approaches
Effect of CYP3A Inhibitors on Mobocertinib: Coadministration of EXKIVITY with multiple doses of itraconazole or ketoconazole (strong CYP3A inhibitors) is predicted to increase the steady-state combined molar AUC of mobocertinib and its active metabolites by 374 to 419%.
Coadministration of EXKIVITY with multiple doses of a moderate CYP3A inhibitor is predicted to increase the steady-state combined molar AUC of mobocertinib and its active metabolites by approximately 100-200%.
Effect of CYP3A Inducers on Mobocertinib: Coadministration of EXKIVITY with multiple doses of rifampin (a strong CYP3A inducer) is predicted to decrease the steady-state combined molar AUC of mobocertinib and its active metabolites by 92%.
Coadministration of EXKIVITY with multiple doses of efavirenz (a moderate CYP3A inducer) is predicted to decrease the steady-state combined molar AUC of mobocertinib and its active metabolites by 58%.
Effect of Mobocertinib on CYP3A Substrates: Coadministration of EXKIVITY 160 mg once daily with oral or intravenous midazolam (a CYP3A substrate) decreased the AUC of midazolam by 32% and 16%, respectively.
Effect of Mobocertinib on P-gp Substrates: No clinically meaningful differences in the pharmacokinetics of digoxin or dabigatran etexilate (P-gp substrates) are predicted when coadministered with multiple doses of EXKIVITY.
Effect of Mobocertinib on BCRP Substrates: The clinical significance of changes in the pharmacokinetics of a BCRP substrate (e.g., sulfasalazine) when coadministered with multiple doses of EXKIVITY is unknown.
In Vitro Studies
CYP Enzymes: Mobocertinib, AP32960, and AP32914 do not inhibit CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, or 2D6 at clinically relevant concentrations.
Transporter Systems: Mobocertinib is an inhibitor of P-gp and BCRP. At clinically relevant concentrations, mobocertinib does not inhibit BSEP, MATE1, MATE2-K, MRP2, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT1, OAT3, OCT1, or OCT2.
Mobocertinib is a substrate of P-gp. Mobocertinib is not a substrate of BCRP, OATP1B1, and OATP1B3.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies were not performed with mobocertinib. Mobocertinib was not mutagenic in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay and did not induce chromosomal aberrations in an in vitro chromosome aberration assay in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Mobocertinib was not clastogenic in an in vivo bone marrow micronucleus test in rats.
Fertility, early embryonic development, and pre- and post-natal toxicology studies were not conducted with mobocertinib; however, in 4- and 13-week repeat-dose toxicology studies in rats and dogs, there were generally reversible changes that included decreases in organ weights affecting multiple reproductive organs (including ovaries, seminal vesicle/prostate gland, and/or uterus) at exposures ≥0.3 times the AUC observed at the recommended clinical dose of 160 mg once daily, as well as microscopic changes of decreased epithelial thickness/inflammation of the cervix/vagina and atrophy of the uterus, prostate gland, or mammary gland (males only) at exposures ≥0.2 times the AUC at the 160 mg once daily clinical dose in rats and/or dogs. Based on these findings, mobocertinib may impair fertility in males and females of reproductive potential. These effects may be reversible.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In rats, mobocertinib administration resulted in histological findings of decreased corneal epithelial thickness in the 4- and 13-week repeat-dose toxicology studies at doses ≥0.8 times the human exposure (AUC) at the 160 mg once daily clinical dose. In the 4-week repeat-dose study in dogs, mobocertinib administration resulted in discharge from the eye, sclera injection, partial or complete closure of the eye and histological findings of corneal epithelial atrophy at doses ≥0.3 times the AUC at the 160 mg once daily clinical dose. In the 13-week repeat-dose study in dogs, mobocertinib administration resulted in discharge, conjunctival hyperemia, and corneal opacity correlating histologically with decreased corneal epithelial thickness at doses ≥0.2 times the AUC at the 160 mg once daily clinical dose. The clinical relevance of these findings is unknown.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of EXKIVITY was evaluated in a pooled subset of patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation-positive metastatic or locally advanced NSCLC whose disease had progressed on or after platinum-based chemotherapy enrolled in an international, open-label, multicohort clinical trial (AP32788-15-101, NCT02716116). Patients had histologically or cytologically confirmed locally advanced or metastatic disease (Stage IIIB or IV) and a documented EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation based on local testing. Patients received EXKIVITY at a dose of 160 mg once daily until disease progression or intolerable toxicity.
In the efficacy population, EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation status was determined by prospective local testing using samples from tumor tissue (87%), plasma (5%), or other specimens such as pleural fluid (8%). Of the 114 patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations, 70% of patient tissue samples were tested retrospectively using Life Technologies Corporation Oncomine Dx™ Target Test. While 75% of patients were positive for EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation, 14% did not have an EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation identified, and 11% did not generate reportable results.
The efficacy population consisted of 114 patients and had the following demographic characteristics: the median age was 60 years (range: 27 to 84 years); 66% were female; 60% were Asian, 37% were White, and 3% were Black; 71% had never smoked; at baseline, 75% had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status 1. At baseline, 99% of patients had metastatic disease, 98% of patients had adenocarcinoma histology and 35% of patients had brain metastases. The median number of prior therapies was 2 (range: 1 to 7) and 43% percent had received prior immunotherapy.
The major efficacy outcome measure was overall response rate (ORR) according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST v1.1) as evaluated by blinded independent central review (BICR). Additional efficacy outcome measures included duration of response (DOR) by BICR.
Efficacy results are summarized in Table 5.
Table 5: Efficacy Results in Patients with EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutation-Positive NSCLC Whose Disease Has Progressed on or after Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Study AP32788-15-101
|
|
EXKIVITY (n=114) |
| Overall Response Rate (ORR)a (95% CI) | 28% (20, 37)b |
| Duration of Response (DOR) | |
| Median (months)c, (95% CI) | 17.5 (7.4, 20.3) |
| Patients with DOR ≥6 monthsd | 59% |
a Per BICR, CI = confidence interval
b All responses were partial responses
c Kaplan-Meier estimate using confirmed responses only
d Based on observed duration of response
Investigator-assessed ORR was 35% (95% CI: 26, 45) with a median DOR of 11.2 months (63% of these patients had observed responses lasting longer than 6 months).
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
EXKIVITY is supplied as 40 mg capsules: white, size 2, imprinted with “MB788” on the cap and “40mg” on the body in black ink.
| Bottle of 90 capsules | NDC 63020-040-90 |
| Bottle of 120 capsules | NDC 63020-040-12 |
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted from 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
QTc Interval Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes
Inform patients of the risk of QTc prolongation. Symptoms that may be indicative of significant QTc
prolongation include dizziness, lightheadedness, and syncope. Advise patients to report these symptoms and to inform their healthcare provider about the use of any heart medications [see
Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis
Inform patients of the risks of severe or fatal ILD/pneumonitis. Advise patients to contact their
healthcare provider immediately to report new or worsening respiratory symptoms such as cough,
shortness of breath or chest pain [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Cardiac Toxicity
Inform patients of the risk of heart failure. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider
immediately if they experience any signs or symptoms of heart failure such as palpitations, shortness
of breath, chest pain, and syncope [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Diarrhea
Inform patients that EXKIVITY may cause diarrhea, which may be severe in some cases and should
be treated promptly. Advise patients to have antidiarrheal medicine readily available and promptly
start antidiarrheal treatment (e.g., loperamide), increase oral fluids and electrolyte intake, and contact
their healthcare provider if diarrhea occurs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to inform their healthcare
provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Use in Specific
Populations (8.1)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective non-hormonal contraception during treatment with EXKIVITY and for 1 month after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with EXKIVITY and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with EXKIVITY and for 1 week after the last dose
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Infertility
Advise females and males of reproductive potential that EXKIVITY may impair fertility [see Use in
Specific Populations (8.3)].
Drug Interactions
Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider of all concomitant medications, including
prescription medicines, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and herbal products [see Drug Interactions
(7)]. Inform patients to avoid grapefruit or grapefruit juice while taking EXKIVITY.
Missed Dose
Advise patients that if a dose of EXKIVITY is missed by 6 hours or if vomiting occurs, resume
treatment as prescribed the next day [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
